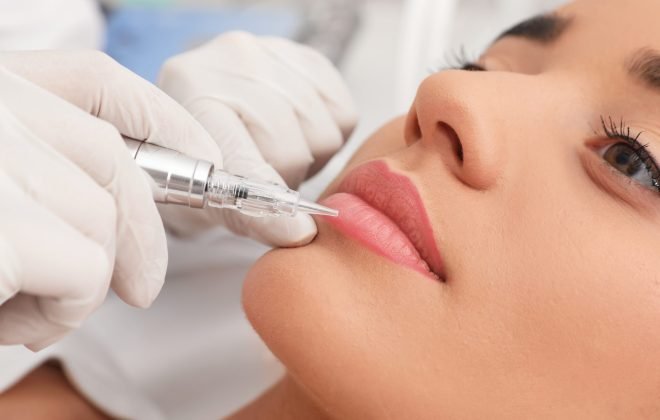
Injectable Beauty

Injectable beauty treatments have revolutionized the cosmetic industry by offering non-surgical solutions for enhancing facial features, reducing signs of aging, and improving skin texture. These treatments are quick, relatively painless, and require little to no downtime, making them highly popular among individuals seeking aesthetic improvements without undergoing invasive procedures.
Breast Augmentation
Breast augmentation, also known as augmentation mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure designed to enhance the size, shape, and overall appearance of the breasts. This procedure is one of the most popular cosmetic surgeries worldwide and is commonly sought by individuals who wish to improve their body contour, restore breast volume lost after weight reduction or pregnancy, and achieve more symmetrical breasts.
Types of Breast Augmentation
- Breast Implants:
- Silicone Implants: Filled with silicone gel, these implants feel more like natural breast tissue and are less likely to ripple.
- Saline Implants: Filled with sterile salt water, these implants can be adjusted for size during surgery and have a uniform shape and feel.
- Structured Saline Implants: These contain an inner structure that makes them feel more natural compared to regular saline implants.
- Fat Transfer:
- Liposuction and Grafting: Fat is harvested from another part of the body (such as the abdomen or thighs) via liposuction, then purified and injected into the breasts to enhance their size and shape.
- Natural Results: Provides a natural look and feel using the patient’s own tissue, and avoids the use of implants.
Buttock Augmentation
Buttock augmentation, commonly referred to as a “butt lift” or “BBL” (Brazilian Butt Lift), is a cosmetic procedure designed to enhance the size, shape, and contour of the buttocks. This procedure is popular among individuals seeking to improve their body proportions and achieve a more voluptuous, youthful appearance.
Types of Buttock Augmentation
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL):
- Fat Transfer: This involves liposuction to remove excess fat from areas such as the abdomen, thighs, or flanks, which is then purified and injected into the buttocks to enhance their size and shape.
- Natural Look and Feel: Uses the patient’s own fat, resulting in a more natural appearance and feel compared to implants.
- Buttock Implants:
- Silicone Implants: Solid or semi-solid silicone implants are surgically placed within the buttocks to increase volume and improve shape.
- Consistent Volume: Provides a reliable and consistent enhancement for those who do not have enough body fat for a BBL.
- Non-Surgical Options:
- Injectable Fillers: Fillers like Sculptra can be used to gradually enhance the buttocks by stimulating collagen production over a series of treatments.
- Less Invasive: Suitable for individuals seeking moderate enhancement without surgery.
Lip Fillers
Lip fillers, also known as lip augmentation or lip injections, are a popular non-surgical cosmetic procedure designed to enhance the volume, shape, and definition of the lips. This treatment involves injecting dermal fillers into the lips to create a fuller, more youthful appearance.
Types of Lip Fillers
- Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Fillers:
- Popular Brands: Juvederm, Restylane, Belotero, and Teosyal.
- Properties: Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance in the body that retains moisture and adds volume. HA fillers are smooth, gel-like substances that are easily absorbed by the body over time.
- Collagen-Based Fillers:
- Less Common: Collagen fillers were once popular but have largely been replaced by HA fillers due to better safety and efficacy profiles.
- Calcium Hydroxylapatite:
- Brand: Radiesse.
- Properties: Thicker than HA fillers, primarily used for deeper lines and wrinkles, but can be used off-label for lips in some cases.
- Poly-L-Lactic Acid:
- Brand: Sculptra.
- Properties: Stimulates collagen production and provides gradual, long-lasting results, but not typically used for immediate lip enhancement.
Earlobe Filler
Earlobe filler is a non-surgical cosmetic procedure designed to restore volume, shape, and youthful appearance to the earlobes. This treatment is particularly beneficial for individuals with stretched, sagging, or deflated earlobes due to aging, wearing heavy earrings, or genetic factors.
Benefits of Earlobe Filler
- Restores Volume and Shape:
- Aesthetic Enhancement: Fills in deflated or sagging earlobes, creating a plumper, more youthful appearance.
- Supports Earrings: Reinforces the earlobe to better support earrings, preventing them from drooping or stretching the earlobe further.
- Non-Surgical and Quick:
- Minimal Downtime: The procedure is quick, typically taking about 15-30 minutes, and involves minimal recovery time.
- Immediate Results: Noticeable improvement in the appearance of the earlobes immediately after the procedure.
- Customizable and Reversible:
- Personalized Treatment: The amount of filler can be adjusted to achieve the desired result.
- Reversible: Hyaluronic acid fillers can be dissolved with hyaluronidase if needed.
Types of Fillers Used
- Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Fillers:
- Popular Brands: Juvederm, Restylane, and Belotero.
- Properties: HA fillers are smooth, gel-like substances that naturally occur in the body, providing hydration and volume. They are easily absorbed over time and offer a natural look and feel.
- Calcium Hydroxylapatite:
- Brand: Radiesse.
- Properties: Thicker and denser than HA fillers, providing longer-lasting results. Suitable for deeper volume restoration.
Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring substance found in the human body, predominantly in the skin, connective tissue, and eyes. It plays a critical role in maintaining skin hydration, elasticity, and overall health. Due to its unique properties, hyaluronic acid is widely used in various medical and cosmetic applications.
Key Properties of Hyaluronic Acid
- Hydration:
- Moisture Retention: HA can hold up to 1,000 times its weight in water, making it an excellent hydrator for the skin.
- Skin Plumpness: By retaining moisture, HA helps keep the skin plump and supple.
- Lubrication:
- Joints and Tissues: HA is a major component of synovial fluid, which lubricates and cushions joints.
- Wound Healing:
- Tissue Repair: HA plays a role in the skin’s natural healing process, promoting tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation.
Benefits of Hyaluronic Acid
- Hydration and Moisture Retention:
- Skin Health: Keeps the skin hydrated, plump, and healthy, reducing dryness and flakiness.
- Improved Elasticity: Enhances skin elasticity and firmness, contributing to a more youthful appearance.
- Non-Allergenic:
- Biocompatibility: Since HA is naturally found in the body, the risk of allergic reactions is minimal, making it a safe option for most people.
- Versatility:
- Wide Range of Uses: HA can be used in various medical and cosmetic applications, from skincare and dermal fillers to joint health and eye care.
Profhilo
Profhilo is an innovative injectable treatment designed to improve skin hydration, elasticity, and overall quality. Unlike traditional dermal fillers, Profhilo is composed of pure hyaluronic acid (HA) and works by bio-remodeling the skin rather than adding volume. This treatment is particularly popular for its natural-looking results and ability to rejuvenate the skin from within.
Key Properties of Profhilo
- High Concentration of Hyaluronic Acid:
- Pure HA: Profhilo contains one of the highest concentrations of hyaluronic acid available in aesthetic treatments, providing intense hydration and stimulation of collagen and elastin production.
- BDDE-Free: It is free of BDDE (butanediol diglycidyl ether), a cross-linking agent used in many other HA fillers, making it a purer form of hyaluronic acid.
- Bio-Remodeling:
- Stimulation of Collagen and Elastin: Profhilo works by spreading evenly through the skin tissue, stimulating the production of collagen and elastin, which improves skin tone, texture, and elasticity.
- Hydration and Firming: The treatment enhances skin hydration and firmness, leading to a smoother, more youthful appearance.
Treatment Areas
Profhilo is primarily used to treat:
- Face: Improves overall skin quality, particularly in areas with visible signs of aging such as fine lines and sagging.
- Neck: Addresses crepey skin and loss of firmness.
- Hands: Enhances skin texture and hydration.
- Décolletage: Improves skin elasticity and appearance.
Sculptra
Sculptra is a poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) injectable treatment designed to gradually restore facial volume and stimulate collagen production, resulting in a natural, youthful appearance. Unlike traditional dermal fillers that provide immediate results, Sculptra works over time to improve skin structure and firmness.
Key Properties of Sculptra
- Poly-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA):
- Biocompatible and Biodegradable: PLLA is a synthetic, biocompatible substance that naturally degrades in the body.
- Collagen Stimulation: It stimulates the body’s own collagen production, leading to gradual and long-lasting improvements in skin volume and texture.
- Gradual Results:
- Natural-Looking Enhancement: Results appear gradually over a series of treatments, providing a subtle, natural-looking enhancement rather than an immediate change.
Treatment Areas
Sculptra is effective for treating various areas of the face that have experienced volume loss due to aging or other factors. Common treatment areas include:
- Cheeks: Restores volume to hollow cheeks.
- Nasolabial Folds: Reduces the appearance of smile lines.
- Marionette Lines: Softens lines around the mouth.
- Jawline: Improves jawline contour.
- Temples: Fills hollow temples.
- Chin: Enhances the chin’s shape and definition.
Mesotherapy
Mesotherapy is a non-surgical cosmetic treatment that involves injecting small amounts of vitamins, enzymes, hormones, and plant extracts into the mesodermal layer of the skin. Developed in France in the 1950s, mesotherapy is used to rejuvenate and tighten skin, as well as to remove excess fat and reduce cellulite.
Key Components of Mesotherapy
- Vitamins and Minerals:
- Nourishment: Provide essential nutrients to improve skin health and appearance.
- Common Ingredients: Vitamins such as A, C, E, and B-complex vitamins.
- Amino Acids:
- Collagen Production: Support the synthesis of collagen and elastin for firmer, more elastic skin.
- Hyaluronic Acid:
- Hydration: Attracts and retains moisture in the skin, enhancing hydration and plumpness.
- Plant Extracts:
- Natural Rejuvenation: Promote skin health with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Enzymes and Hormones:
- Fat Reduction: Aid in breaking down fat cells and stimulating metabolism.
Treatment Areas
Mesotherapy is versatile and can be used on various parts of the body, including:
- Face and Neck: For skin rejuvenation, reducing fine lines and improving overall texture.
- Body: To reduce localized fat deposits and cellulite in areas such as the abdomen, thighs, hips, and arms.
- Scalp: To promote hair growth and improve scalp health.
Placenta Injection
Placenta injections, also known as placenta therapy, involve the administration of extracts derived from human or animal placental tissue to promote health, rejuvenation, and aesthetic improvement. This therapy has a long history, particularly in traditional medicine, and is gaining popularity in modern aesthetic and anti-aging treatments due to its potential benefits for skin, hair, and overall vitality.
Key Components of Placenta Injections
Placenta injections contain a rich array of bioactive substances, including:
- Growth Factors:
- Cell Regeneration: Promote the growth and repair of cells and tissues.
- Hormones:
- Regulation and Balance: Support hormonal balance and overall health.
- Amino Acids:
- Protein Synthesis: Essential for building proteins and promoting cell repair.
- Vitamins and Minerals:
- Nutrient Supply: Provide essential nutrients for skin health and vitality.
- Enzymes:
- Metabolic Enhancement: Support various metabolic processes in the body.
Benefits of Placenta Injections
- Skin Rejuvenation:
- Improved Elasticity and Firmness: Enhances skin elasticity, reducing sagging and promoting a firmer appearance.
- Reduction of Fine Lines and Wrinkles: Smoothens fine lines and wrinkles by stimulating collagen production.
- Hydration and Radiance: Increases skin hydration, leading to a more radiant and youthful complexion.
- Anti-Aging Effects:
- Cell Renewal: Encourages the regeneration of cells, contributing to a more youthful appearance.
- Antioxidant Properties: Protects against oxidative stress and environmental damage.
- Hair Restoration:
- Hair Growth Stimulation: Promotes hair growth and strengthens hair follicles, addressing hair thinning and loss.
- Scalp Health: Improves overall scalp health, creating a better environment for hair growth.
- General Health and Vitality:
- Energy and Well-being: Enhances overall energy levels and sense of well-being.
- Immune Support: Boosts the immune system, aiding in overall health maintenance.
Treatment Areas
Placenta injections can be used for various purposes and areas, including:
- Facial Rejuvenation: To improve skin texture, elasticity, and appearance.
- Hair and Scalp Treatment: To promote hair growth and improve scalp health.
- Overall Wellness: For general anti-aging and vitality enhancement.
Botulinum Toxin
Botulinum toxin, commonly known by brand names such as Botox, Dysport, and Xeomin, is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It is widely used in cosmetic and medical treatments to temporarily reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines by inhibiting muscle activity. Beyond aesthetics, it has numerous therapeutic applications for various medical conditions.
Key Properties of Botulinum Toxin
- Neurotoxin Mechanism:
- Muscle Relaxation: Botulinum toxin works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contractions. This results in temporary muscle paralysis, leading to a reduction in wrinkles and fine lines.
- Temporary Effects:
- Duration: The effects of botulinum toxin typically last between three to six months, after which muscle activity gradually returns.
Cosmetic Applications
Botulinum toxin is primarily used in cosmetic dermatology to address facial wrinkles and fine lines. Common treatment areas include:
- Forehead Lines: Horizontal lines that form on the forehead.
- Frown Lines: Vertical lines between the eyebrows, also known as glabellar lines.
- Crow’s Feet: Lines that appear at the outer corners of the eyes.
- Bunny Lines: Lines that form on the bridge of the nose.
- Lip Lines: Vertical lines around the mouth, also known as smoker’s lines.
- Neck Bands: Horizontal lines on the neck, also known as platysmal bands.
Medical Applications
Beyond aesthetics, botulinum toxin has numerous therapeutic uses:
- Chronic Migraines: Helps reduce the frequency and severity of migraine headaches.
- Hyperhidrosis: Treats excessive sweating by blocking the nerves that activate sweat glands.
- Muscle Spasticity: Manages muscle stiffness and spasms in conditions like cerebral palsy and multiple sclerosis.
- Overactive Bladder: Reduces urinary incontinence by relaxing the bladder muscles.
- Strabismus: Corrects crossed eyes by relaxing overactive eye muscles.
- Blepharospasm: Treats involuntary blinking and eyelid spasms.
PRP Hair Loss Treatment
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy for hair loss is a non-surgical treatment that uses the patient’s own blood plasma enriched with platelets to stimulate hair growth. PRP therapy has gained popularity as a natural and effective option for both men and women experiencing hair thinning or hair loss.
Key Components of PRP Therapy
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP):
- Blood Plasma Enriched with Platelets: PRP is obtained by drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood and processing it to concentrate the platelets.
- Growth Factors: Platelets contain growth factors such as PDGF (Platelet-Derived Growth Factor), VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor), and TGF (Transforming Growth Factor), which promote tissue repair and regeneration.
Mechanism of Action
- Hair Follicle Stimulation:
- Cell Growth and Repair: PRP is injected into the scalp at the level of the hair follicles to stimulate hair growth by promoting cell proliferation and repair processes.
- Increased Blood Supply: Enhances blood circulation to the hair follicles, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen.
Treatment Process
- Consultation and Assessment:
- Evaluation: A thorough evaluation of the patient’s hair loss pattern and medical history to determine the suitability for PRP therapy.
- Expectations: Discussion of expected outcomes and realistic goals.
- PRP Collection and Preparation:
- Blood Draw: A small amount of blood (similar to a standard blood test) is drawn from the patient.
- Centrifugation: The blood is processed in a centrifuge machine to separate the PRP from other components of the blood.
- Activation: Optionally, the PRP may be activated with calcium chloride or another activator to release growth factors.
- PRP Injection:
- Local Anesthesia: Some practitioners may apply a topical anesthetic to numb the scalp and minimize discomfort during the injections.
- Injection Process: The PRP is injected into the scalp using a fine needle, typically targeting areas of hair thinning or loss.
- Multiple Injections: The injections are spaced across the scalp according to the treatment plan.
Recovery and Aftercare
- Post-Treatment Care:
- Minimal Downtime: Most patients can resume normal activities immediately after PRP therapy.
- Avoiding Irritants: Patients are advised to avoid vigorous activity, excessive sun exposure, and hair treatments for the first few days post-treatment.
- Follow-Up Sessions:
- Treatment Schedule: A series of PRP sessions may be recommended, usually spaced about 4-6 weeks apart, followed by maintenance treatments every few months.
- Assessment: Regular follow-up visits to assess progress and adjust the treatment plan if needed.
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy has emerged as a popular anti-aging treatment due to its ability to promote skin rejuvenation, enhance collagen production, and improve overall skin texture and tone. Here’s a comprehensive overview of PRP anti-aging treatment:
Key Components of PRP Therapy
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP):
- PRP is derived from the patient’s own blood. It contains a concentrated amount of platelets, growth factors, and other bioactive proteins that play a key role in tissue repair and regeneration.
Mechanism of Action
- Stimulation of Collagen and Elastin:
- When PRP is applied to the skin or injected into targeted areas, the growth factors stimulate collagen and elastin production. Collagen provides structural support to the skin, while elastin maintains its elasticity and firmness.
- Cellular Renewal and Regeneration:
- PRP promotes cellular turnover and regeneration, leading to improved skin texture, reduced fine lines, and a more youthful appearance.
Treatment Process
- Consultation and Assessment:
- A consultation with a qualified practitioner to discuss skin concerns, aesthetic goals, and determine the suitability of PRP therapy.
- PRP Collection and Preparation:
- A small amount of blood is drawn from the patient.
- The blood is processed using a centrifuge to separate and concentrate the platelets and growth factors.
- The resulting PRP is prepared for application or injection.
- Application or Injection:
- Topical Application: PRP may be applied directly to the skin after microneedling or other skin rejuvenation procedures. This allows for better absorption of growth factors into the skin layers.
- Injection: PRP can also be injected into specific areas of the face or neck where aging signs are prominent, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and areas of volume loss.
Recovery and Aftercare
- Post-Treatment Care:
- Minimal downtime: Patients can usually resume normal activities immediately after treatment.
- Some redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection sites may occur, which typically resolves within a few days.
- Follow-Up Sessions:
- A series of PRP treatments spaced several weeks apart may be recommended for optimal results.
- Maintenance treatments every few months can help sustain improvements in skin quality and appearance.
Benefits of PRP Anti-Aging Treatment
- Natural Approach:
- PRP utilizes the patient’s own blood, reducing the risk of allergic reactions or adverse effects.
- Skin Rejuvenation:
- Improves skin texture, tone, and firmness.
- Reduces fine lines, wrinkles, and other signs of aging.
- Collagen Boosting:
- Stimulates collagen synthesis, enhancing skin elasticity and resilience.
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy has been explored for its potential benefits in sexual health treatments, particularly for both men and women seeking to enhance sexual function and satisfaction. Here’s an overview of PRP sexual health treatment:
Key Components of PRP Therapy
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP):
- PRP is derived from the patient’s own blood. It contains a concentrated amount of platelets, growth factors, and other bioactive proteins that promote tissue repair and regeneration.
Applications in Sexual Health
PRP therapy for sexual health primarily focuses on improving blood flow, tissue regeneration, and sensitivity in genital areas, aiming to enhance sexual function and pleasure.
For Men:
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED) Treatment:
- PRP injections into the penis can potentially stimulate new tissue growth and improve blood flow.
- The growth factors in PRP may promote the regeneration of blood vessels and nerve tissue, which are crucial for achieving and maintaining erections.
- Peyronie’s Disease:
- PRP injections may help reduce the curvature of the penis associated with Peyronie’s disease, a condition characterized by fibrous scar tissue formation in the penis.
For Women:
- Female Sexual Dysfunction:
- PRP injections into the vaginal area, specifically the G-spot and clitoris, can improve blood flow, sensitivity, and lubrication.
- This can potentially enhance sexual arousal, orgasm intensity, and overall sexual satisfaction.
Treatment Process
- Consultation and Assessment:
- A comprehensive evaluation by a qualified practitioner to discuss sexual health concerns, assess medical history, and determine the suitability of PRP therapy.
- PRP Collection and Preparation:
- A small amount of blood is drawn from the patient.
- The blood is processed using a centrifuge to concentrate the platelets and growth factors into PRP.
- Injection Procedure:
- For Men: PRP is injected into specific areas of the penis, such as the corpora cavernosa, where it can potentially improve erectile function and tissue health.
- For Women: PRP is injected into the vaginal walls, clitoris, or G-spot to enhance sensitivity and sexual response.
Recovery and Aftercare
- Post-Treatment Care:
- Patients may experience minor discomfort, swelling, or bruising at the injection sites, which typically resolves within a few days.
- Normal activities can usually be resumed shortly after treatment.
- Follow-Up Sessions:
- A series of PRP treatments spaced several weeks apart may be recommended for optimal results.
- Maintenance treatments may be necessary to sustain improvements in sexual function and satisfaction.
Benefits of PRP Sexual Health Treatment
- Natural Approach:
- PRP uses the patient’s own blood, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions or adverse effects.
- Improvement in Sexual Function:
- Enhances erectile function in men.
- Improves sensitivity and arousal in women.
- Non-Invasive and Safe:
- Minimally invasive procedure with minimal downtime.
IV Therapy, also known as intravenous therapy, involves administering fluids, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients directly into the bloodstream through an IV drip. This method allows for rapid absorption and delivery of essential nutrients to the body. Here’s an overview of IV Therapy:
Key Components of IV Therapy
- Nutrient Solutions:
- IV fluids are typically a combination of saline solution (saltwater) and electrolytes to maintain hydration and balance.
- Additional components may include vitamins (such as vitamin C, B vitamins), minerals (like magnesium, calcium), antioxidants (such as glutathione), and amino acids.
Purpose and Benefits
IV Therapy is used for various purposes, including:
- Hydration:
- Replenishing fluids and electrolytes quickly, especially beneficial for individuals who are dehydrated or unable to take fluids orally.
- Nutrient Boost:
- Providing a concentrated dose of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants directly into the bloodstream for immediate use by cells throughout the body.
- Health and Wellness:
- Supporting overall well-being, immune function, and energy levels.
- Promoting faster recovery from illness, fatigue, or strenuous activities.
- Athletic Performance:
- Enhancing hydration and providing nutrients to support athletic recovery and performance.
Types of IV Therapy
- Hydration IV:
- Contains saline solution and electrolytes to restore hydration levels quickly.
- Vitamin IV:
- Includes high doses of vitamins, such as vitamin C, B vitamins (like B12), and other nutrients to boost immune function, energy levels, and overall health.
- Antioxidant IV:
- Contains antioxidants like glutathione or vitamins (such as vitamin C) to neutralize free radicals and support cellular health.
- Performance IV:
- Designed for athletes to replenish fluids, electrolytes, and nutrients lost during intense workouts or competitions.
Treatment Process
- Consultation:
- Evaluation of the patient’s health status, concerns, and goals to determine the appropriate IV therapy regimen.
- IV Administration:
- A small catheter (IV line) is inserted into a vein, typically in the arm.
- The nutrient solution is administered gradually over a period of time, monitored by a healthcare professional.
- Monitoring and Adjustments:
- Vital signs and patient response are monitored during the infusion to ensure safety and effectiveness.
- Adjustments may be made based on individual tolerance and needs.